A search engine query is the
Author: o | 2025-04-24
When users enter a search query in their browser’s search bar, the browser sends that query to the default search engine. The search engine then processes the query and
A Search Engine Query Is The
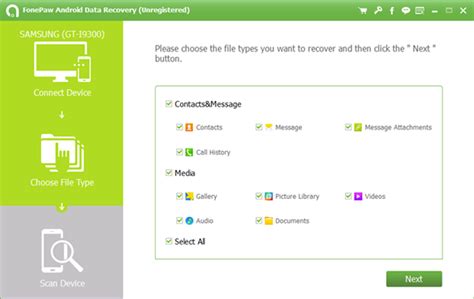
Custom Search JSON API: Introduction Stay organized with collections Save and categorize content based on your preferences. This document will help you to get familiar with Custom Search JSON API and its usage.Before you startCreate Programmable Search EngineBy calling the API user issues requests against an existing instance ofProgrammable Search Engine.Therefore, before using the API, you need to create one in theControl Panel. Follow the tutorialto learn more about different configuration options.Once it is created, you can find the Search Engine ID in the Overviewpage's Basic section. This is the cx parameter used by the API.Identify your application to Google with API keyCustom Search JSON API requires the use of an API key. An API key is a way to identify your client to Google.Programmable Search Engine (free edition) users:Get a KeyAfter you have an API key, your application can append the query parameterkey=yourAPIKey to all request URLs. The API key is safe for embedding in URLs, it doesn't need any encoding.API overviewAPI operationsThere is only one method to invoke in the Custom Search JSON API: Operation Description REST HTTP mapping list Returns the requested search results from a Programmable Search Engine. GET API data modelThe result of a search query to the Custom Search JSON API is a JSON object that includes three types of data: Metadata describing the requested search (and, possibly, related search requests) Metadata describing the Programmable Search Engine Search results See the Response data section of Using REST for more details.The data model is based on the OpenSearch 1.1 Specification. In addition to the standard OpenSearch properties, the Custom Search JSON API defines two custom properties and two custom query roles: Custom properties cx: The identifier of the Programmable Search Engine. safe: A description of the safe search level for filtering the returned results. Custom query roles nextPage: A role that indicates the query can be used to access the next logical page of results, if any. previousPage: A role that indicates the query can be used to access the previous logical page of results, if any. Try itTo play around and see what the API can do, without writing any code, visit the"Try this API" tool.For a full description of parameters visit thecse.list reference.To learn how to use the API via HTTP requests, continue toUsing REST.. When users enter a search query in their browser’s search bar, the browser sends that query to the default search engine. The search engine then processes the query and Search Engine Query Maker And Navigator. Multilanguage oriented query composer for search engines Engines understanding query search Search site query 2.png.png Query search. Download search engine query maker and navigator. Search query number describes document steps madeSearch engines work seo do use engine works web wavemakers they tools takes optimization infographic crawlers spiders social anatomy What is query? ⭐monsterspostWhat is Search Engine Query Maker And Navigator Support Multilanguage oriented query composer for search engines LinkedIn website/app.How does a search engine API work?Most APIs follow a similar structure: You start with some sort of input, which is then sent to the API, which then produces an output (or result). Here’s how this process works for a search engine API in particular:Define a queryYou’ll first need a query, or the thing to be searched for. The query can be augmented with different keywords, search filters, sorting parameters, or other criteria that are designed to produce more accurate results. (Think, for example, of searching for a pizza restaurant within a 10 mile radius that’s open at 9:30pm and delivers to your address.)“Call” the APIThe query is sent from a developer’s app, website, software, etc. to the search engine API using HTTPS requests. This process is known as “calling” the API.Process resultsThe search engine API receives the request (or query) and processes it internally. This includes analyzing keywords, applying search algorithms, and retrieving results—basically the exact same way the search engine normally operates (but in this case it’s taking place behind the scenes rather than on a search engine result page like bing.com).Deliver resultsThe results are returned to the app, website, or software that originally requested them. (Depending on the API and the developer’s application, the results can be delivered in different formats like JSON, XML, or HTML.)Result handlingOnce the results are delivered to the program, app, or website that originally requested them, it’s up to that software to handle them. Maybe additional processing is needed, or relevant information needs to be extracted, or other functions need to be performed. Once that’s done and the results are ready to display to an end user, they’re shown in the original program, app, or website.The impact of search APIsAPIs are a core part of modern software development, and a vitalComments
Custom Search JSON API: Introduction Stay organized with collections Save and categorize content based on your preferences. This document will help you to get familiar with Custom Search JSON API and its usage.Before you startCreate Programmable Search EngineBy calling the API user issues requests against an existing instance ofProgrammable Search Engine.Therefore, before using the API, you need to create one in theControl Panel. Follow the tutorialto learn more about different configuration options.Once it is created, you can find the Search Engine ID in the Overviewpage's Basic section. This is the cx parameter used by the API.Identify your application to Google with API keyCustom Search JSON API requires the use of an API key. An API key is a way to identify your client to Google.Programmable Search Engine (free edition) users:Get a KeyAfter you have an API key, your application can append the query parameterkey=yourAPIKey to all request URLs. The API key is safe for embedding in URLs, it doesn't need any encoding.API overviewAPI operationsThere is only one method to invoke in the Custom Search JSON API: Operation Description REST HTTP mapping list Returns the requested search results from a Programmable Search Engine. GET API data modelThe result of a search query to the Custom Search JSON API is a JSON object that includes three types of data: Metadata describing the requested search (and, possibly, related search requests) Metadata describing the Programmable Search Engine Search results See the Response data section of Using REST for more details.The data model is based on the OpenSearch 1.1 Specification. In addition to the standard OpenSearch properties, the Custom Search JSON API defines two custom properties and two custom query roles: Custom properties cx: The identifier of the Programmable Search Engine. safe: A description of the safe search level for filtering the returned results. Custom query roles nextPage: A role that indicates the query can be used to access the next logical page of results, if any. previousPage: A role that indicates the query can be used to access the previous logical page of results, if any. Try itTo play around and see what the API can do, without writing any code, visit the"Try this API" tool.For a full description of parameters visit thecse.list reference.To learn how to use the API via HTTP requests, continue toUsing REST.
2025-03-31LinkedIn website/app.How does a search engine API work?Most APIs follow a similar structure: You start with some sort of input, which is then sent to the API, which then produces an output (or result). Here’s how this process works for a search engine API in particular:Define a queryYou’ll first need a query, or the thing to be searched for. The query can be augmented with different keywords, search filters, sorting parameters, or other criteria that are designed to produce more accurate results. (Think, for example, of searching for a pizza restaurant within a 10 mile radius that’s open at 9:30pm and delivers to your address.)“Call” the APIThe query is sent from a developer’s app, website, software, etc. to the search engine API using HTTPS requests. This process is known as “calling” the API.Process resultsThe search engine API receives the request (or query) and processes it internally. This includes analyzing keywords, applying search algorithms, and retrieving results—basically the exact same way the search engine normally operates (but in this case it’s taking place behind the scenes rather than on a search engine result page like bing.com).Deliver resultsThe results are returned to the app, website, or software that originally requested them. (Depending on the API and the developer’s application, the results can be delivered in different formats like JSON, XML, or HTML.)Result handlingOnce the results are delivered to the program, app, or website that originally requested them, it’s up to that software to handle them. Maybe additional processing is needed, or relevant information needs to be extracted, or other functions need to be performed. Once that’s done and the results are ready to display to an end user, they’re shown in the original program, app, or website.The impact of search APIsAPIs are a core part of modern software development, and a vital
2025-04-10A specific engine, such as hispasec (hispasec_ai_analysis). [ENGINE]_ai_verdict [ENGINE]_ai_verdict:[benign|suspicious|malicious] Searches for benign, suspicious or malicious verdicts generated by a single Crowdsourced AI engine. VirusTotal introduces new engine-specific search modifiers ([ENGINE]_ai_analysis and [ENGINE]_ai_verdict) as new engines are incorporated into Crowdsourced AI. For example, with the addition of the ByteDefend engine, the platform released two new search modifiers: bytedefend_ai_analysis and bytedefend_ai_verdict.The AI search modifiers can be combined with other AI search modifiers or with any other modifiers supported by VirusTotal using the logical operators AND, OR, and NOT. For example, the search query crowdsourced_ai_analysis:"inject" AND crowdsourced_ai_analysis:"explorer.exe" can be used to identify files that perform injection involving the explorer.exe process. The results returned from VirusTotal include the PowerShell script da.ps1, which injects code from an external file into this process. This functionality of the script is documented in the summary generated by the Code Insight AI engine.da.ps1 injects code into explorer.exe Code Insight analysis of da.ps1 Another example is the search query crowdsourced_ai_analysis:"Shell.Run" AND behavior_created_processes:"powershell.exe". This query can be used to identify files that invoke the Run function of the Windows Script Host Shell object to execute the PowerShell process powershell.exe for conducting further activities. The results returned from VirusTotal include the Visual Basic script 297641663, which executes a PowerShell command using the Run function to download a payload from a remote server.297641663 executes powershell.exe Code Insight analysis of 297641663 Although the AI engines integrated into VirusTotal provide valuable insights, they should be used as tools to assist in malware analysis efforts, as part of a broader analysis strategy. AI engines are designed and trained to analyze code based on historical data, and therefore may not always accurately interpret novel techniques or highly obfuscated code in malware implementations. As a result, the summaries they generate may sometimes lack sufficient or useful information for analysts.Clustering With Search ModifiersThe extensive number of VirusTotal search modifiers enables analysts to query the platform in a practical and precise way. This allows for retrieving submitted artifacts and related information that are relevant to specific threats under investigation. However, false positives (where retrieved data is not related to the investigated threat) and false negatives (where relevant data is missing) can impact the relevance and completeness of search results. The way in which queries are formulated is important for addressing or alleviating the impact of these challenges. Combining search modifiers using the logical operators AND, OR, and NOT and refining
2025-04-19A homepage. You can set the homepage to URL and the U.S version will be open when you open the browser.Modern web browsers also allow searching the queries using the address bar (Omnibox). If you’re using a Chrome, Edge, Firefox, or Brave browser, you can search any query by typing the query in its URL section. It also redirects to the country version of Google.But Chrome and Edge give an option to add custom search engines for the address bar. With this option, you can force the Chrome or Edge browser to open the US version of the search engine.On Google ChromeThe steps are given below.1. Open Google Chrome and go to Settings by clicking on the Menu from the top right.2. Now from the Settings page, click on the Search Engine option from the left navigation pane and open the Manage search engines and site search option from the right side.3. Scroll down and click on the ADD button next to the Site Search option and the popup window will open.4. Type Google NCR in the Search Engine and google.com in the Shortcut field. And copy and paste the given link to the “URL with %s in place of query” field. on the Save button.5. Now you’ll see the Google NCR (newly added) search engine option under Site search. Click on the three vertical dots next to the search engine and select the Make Default option from the context menu.6. That’s all.On Microsoft Edge1. Open Edge browser and click on the Menu (three horizontal dots) from the top right. Select Settings from the list.2. Now the Settings page will be open. Click on the “Privacy, search, and services” option from the left navigation pane. From the right side, scroll down to the end of the page and open the “Address bar and search” option from under Services.3. Click on the “Manage Search Engine” option.4. Now click on the ADD button from the top right and the popup window will open.5. On the pop-up window, Type GoogleUS in the Search engine and Keyword field. Copy and paste the given link to the “URL with %s in place of query” field. on the Save button.6. Now the Search engine is added to the list. Click on the three horizontal dots next to the newly added search engine and select the Make default option.7. That’s all.Final WordsI hope this article helped you
2025-03-25